How to Differentiate Between Types of Hearing Tests
Hearing tests might seem like a complex puzzle, filled with different
By: admin | July 24, 2024
Hearing tests might seem like a complex puzzle, filled with different steps and options. There are many types of tests, each designed to examine different aspects of your hearing health. To manage your hearing loss effectively, it’s essential to understand these tests. From pure-tone tests to speech audiometry, each test gives unique insights into your hearing abilities. Knowing about these various types will help you when discussing potential treatment options with your audiologist.
A typical hearing test starts with a comprehensive case history. You’ll be asked about your medical history, lifestyle and any specific concerns or symptoms related to your hearing. This information helps the audiologist tailor the test to your needs.
Then comes the actual testing phase. A common test is the pure-tone audiometry, which measures how well you can hear sounds at different pitches and volumes. Another is speech audiometry that checks how well you understand spoken words at different volumes. These tests, conducted in a safe and controlled environment, are part of a broader assessment of your overall hearing health. The results will indicate if there’s any hearing loss and guide potential treatment options.
Hearing tests are crucial for your overall health. They’re more than just measuring your ability to hear different sounds. They offer valuable insights into your hearing health and can even identify potential issues before they become serious problems.
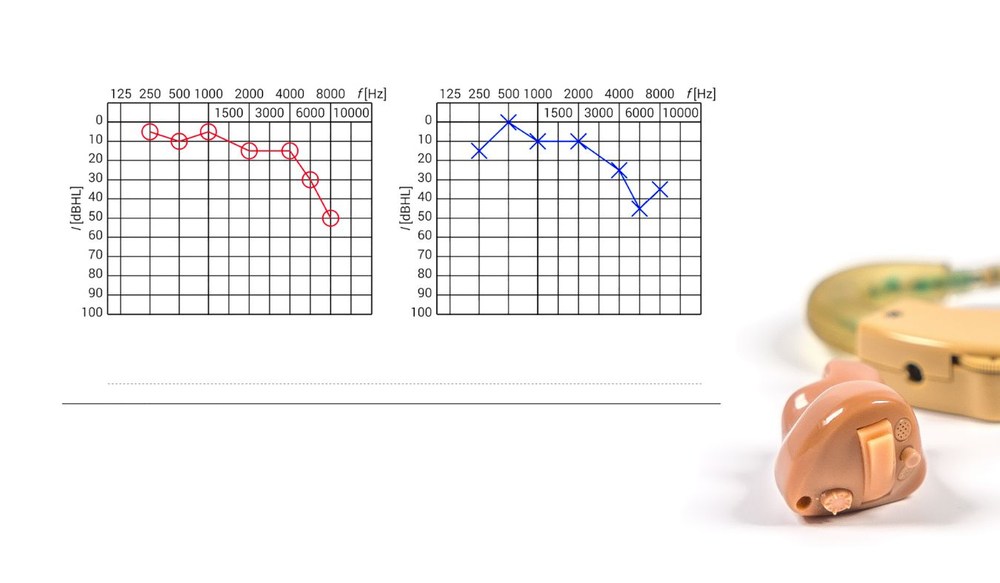
Pure-tone audiometry is a fundamental tool used by audiologists to assess your ability to hear different pitches and volumes. This test involves listening to a series of tones at varying frequencies and volumes through headphones, allowing the audiologist to determine the quietest sounds you can hear at each frequency.
Considered one of the most common hearing assessments, pure-tone audiometry is featured in nearly 90% of all hearing evaluations globally. Its widespread use underscores its significance in diagnosing hearing loss and tailoring appropriate treatments. By providing a detailed profile of your hearing abilities, this test helps in identifying specific types of hearing loss, whether it’s related to high or low frequencies or varying sound intensities.
The results from pure-tone audiometry are crucial for understanding the nature and extent of hearing loss. This information not only guides audiologists in recommending hearing aids or other interventions but also assists in monitoring changes in hearing over time. Overall, pure-tone audiometry plays a central role in managing and improving hearing health.
Speech audiometry is a critical component of a thorough hearing evaluation, offering valuable insights beyond what pure-tone audiometry provides. While pure-tone audiometry assesses your ability to detect different pitches and volumes of sounds, speech audiometry focuses on your ability to understand and process spoken words.
During speech audiometry, you’ll be asked to listen to and repeat words or sentences presented at various volumes. This test evaluates how well you can hear and comprehend speech in different listening conditions, like in quiet environments or amid background noise. The results reveal not just the sensitivity of your hearing but also the clarity of your speech understanding, which is crucial for effective communication.
This test is particularly useful for determining how hearing loss affects everyday conversations and social interactions. For instance, it can highlight difficulties in distinguishing between similar-sounding words or understanding speech in noisy settings.
Tympanometry is a crucial aspect of a thorough hearing evaluation, providing valuable insights into the health and functionality of the middle ear. This test assesses how well the eardrum (tympanic membrane) and the tiny bones in the middle ear—known as ossicles—are working.
During tympanometry, a small probe is placed in the ear canal, and it measures the movement of the eardrum in response to changes in air pressure. By varying the pressure and recording how the eardrum responds, tympanometry can reveal important information about the middle ear’s condition. For instance, it can identify if the eardrum is stiff or not moving properly, which might indicate fluid in the middle ear, a perforated eardrum or issues with the ossicles.
This test is particularly useful in diagnosing conductive hearing loss, which is caused by problems in the middle ear that block sound from reaching the inner ear. Tympanometry can help detect conditions such as otitis media (middle ear infection) or Eustachian tube dysfunction, which can affect hearing by impacting the movement of sound through the ear.
However, tympanometry has limitations. It does not assess the function of the inner ear or the auditory nerve, so it is less effective in detecting sensorineural hearing loss, which originates from damage to the inner ear or the auditory nerve pathways. For a complete picture of hearing health, tympanometry is usually combined with other tests, like pure-tone audiometry and speech audiometry, to provide a comprehensive assessment of hearing abilities and guide appropriate treatment.
Otoacoustic emissions (OAEs) provide a specialized and valuable insight into the health of your inner ear, specifically the cochlea, which is essential for hearing. This test measures the sounds produced by the inner ear in response to external auditory stimuli, offering a unique way to assess cochlear function.
When the inner ear is exposed to a sound stimulus, the hair cells in the cochlea generate tiny, measurable sounds called otoacoustic emissions. These emissions are essentially echoes that reflect the activity and health of these hair cells. Healthy hair cells produce strong, detectable otoacoustic emissions, indicating that the cochlea is functioning properly and is capable of amplifying sound efficiently.
The presence and strength of these otoacoustic emissions provide audiologists with crucial information about your cochlea’s functionality. If the emissions are present and robust, it suggests that the hair cells are working well and that the outer hair cells of the cochlea are functioning as they should. This is often an indication of normal hearing sensitivity.
Conversely, if otoacoustic emissions are absent or significantly weakened, it may signal potential issues with your hearing. This can be indicative of damage or dysfunction in the hair cells of the cochlea, which could be a sign of hearing loss or cochlear abnormalities. While OAEs cannot determine the exact degree of hearing loss or diagnose all types of hearing issues, they are an important part of a comprehensive hearing assessment.
Otoacoustic emissions testing is particularly useful in newborns, young children and individuals who cannot provide verbal feedback during hearing tests. It is a non-invasive, quick and reliable method to screen for hearing problems and to monitor the function of the cochlea over time. By integrating OAEs with other hearing tests, audiologists can gain a well-rounded understanding of your hearing health and make informed decisions about potential treatments or interventions.
Auditory brainstem response testing delves deeper into the complexities of your hearing system, specifically the electrical activity of your auditory nerve and brainstem.
Auditory brainstem response testing records the electrical waves produced by your auditory nerve and brainstem in response to sounds. This information can be crucial for diagnosing issues like hearing loss or neurological problems that might affect your hearing.
This test provides detailed data that can guide hearing loss treatment strategies and help you maintain optimal hearing health. Understanding these tests is crucial to being proactive about your hearing health and making informed decisions about care and treatment. So next time you’re at a hearing clinic, don’t hesitate to ask about auditory brainstem response testing!
The bone conduction test is unique as it bypasses the outer and middle ear, directly stimulating the inner ear. This allows your audiologist to pinpoint whether your hearing loss is conductive (caused by issues in the outer or middle ear) or sensorineural (due to problems in the inner ear). Understanding this distinction is vital for tailoring an effective treatment plan.
In a bone conduction test, a small device placed on your mastoid bone sends vibrations directly to your inner ear. This process helps identify where exactly your hearing issues lie, providing valuable information for managing your hearing health effectively.
Understanding how different assessments work together can provide a comprehensive picture of your auditory capabilities.
Each test conducted during a hearing evaluation plays a significant role in assessing different aspects of your hearing health. For instance, pure-tone audiometry and speech audiometry measure your ability to hear and understand sounds at varying pitches and volumes, while tympanometry and otoacoustic emissions provide insights into the health of your middle ear and inner ear, respectively. Additionally, auditory brainstem response testing examines the electrical activity of your auditory nerve and brainstem.
When combined, these tests offer a detailed understanding of how well you can hear and where any potential issues may lie. This comprehensive approach is key to tailoring an effective treatment plan for you. Regular check-ups with your audiologist are important for maintaining optimal hearing health. So next time you visit your hearing clinic, feel free to ask about these different tests – gaining knowledge is empowering!
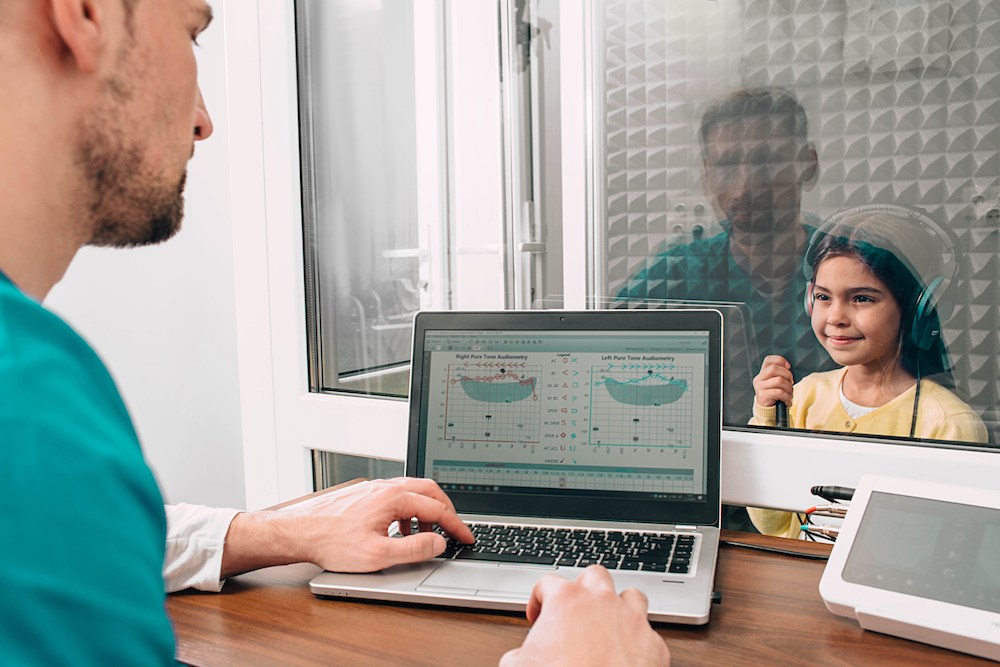
When you meet with your audiologist to discuss your hearing test results, you can expect a detailed and clear explanation of what the findings mean for your hearing health. The audiologist will review the results from various tests, like pure-tone audiometry, speech audiometry and tympanometry, to provide a comprehensive picture of your auditory function.
The discussion typically begins with an overview of your test results, including your hearing thresholds at different frequencies and any patterns of hearing loss that were identified. Your audiologist will explain how these results relate to your ability to hear and understand different sounds and speech. They will also interpret any specific issues detected, like conductive, sensorineural or mixed hearing loss, and how these might be affecting your daily life.
If necessary, your audiologist will use visual aids, like graphs or charts from the test results, to help you better understand your hearing profile. They will describe the implications of your results in practical terms, including how hearing loss might impact your communication, social interactions and overall quality of life.
After gaining a clear understanding of your test results, the next step is to comprehend the potential treatment options. These are largely determined by your specific hearing needs, which have been identified through the tests you’ve undergone.
Hearing aids are the most commonly recommended treatment for hearing loss by audiologists. These devices come in a myriad of styles and are tailored to fit your specific needs, whether you’re looking for something easy-to-handle that can be equipped with powerful features or prefer something smaller that is harder to see. Your audiologist will explain your options in full detail and will help you narrow down your options based on your hearing loss, lifestyle and budget needs.
At Hear In MetroWest, we’re committed to helping you navigate this path towards optimal hearing health. Our dedicated team of professionals is ready to answer any questions and provide further information about these tests or any other concerns related to your hearing health. Give us a call at (774) 375-0373 to schedule an appointment at our Framingham, MA office.

Hearing tests might seem like a complex puzzle, filled with different
By: admin | July 24, 2024

Air travel can be a thrilling experience, but if you’re dealing with
By: admin | April 30, 2024

The significance of your occupation in relation to your hearing health is
By: admin | March 26, 2024
